The following is a brief glossary of common terms related to vasectomy, vasectomy reversal and related topics.
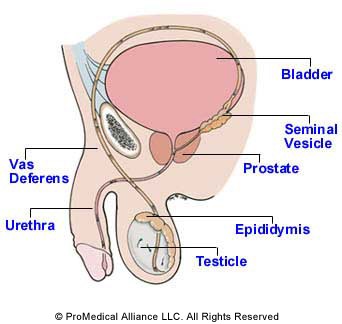
The Male Reproductive Anatomy
Here Is a simple diagram that illustrates the primary elements of the male reproductive system.
A Brief Glossary of Terms
| [A – C] | [D – H] | [I – L] | [M – O] | [P – R] | [S] | [T – U] | [V – Z] |
Some of the terms used throughout this site are briefly defined in the following list. Consult your doctor for a complete explanation or clarification.
Allergic Reaction - the itching and hives some men may experience as an allergic reaction to local or general anesthetic.
Antisperm Antibodies - Antibodies which form against ones own sperm once blood and sperm come in contact (usually during a vasectomy). These antibodies can bind onto the sperm and prevent them from fertilizing eggs, but they cause no health risks or symptoms otherwise.
Artificial Insemination - a procedure that involves the placement of relatively large numbers of healthy sperm either at the entrance of the cervix or into a womens uterus, bypassing the cervix, to have direct access to the fallopian tubes.
Assisted Reproduction Techniques (ART) - new forms of treatment for male and female infertility. Includes sperm retrieval, artificial insemination, in vitro fertilization and sperm microinjection (termed Intra-Cytoplasmic Sperm Injection).
Back to top
Bladder - a muscular, elastic pouch that serves to store and expel urine.
Chronic Orchalgia - a rarely experienced dull ache in the testicles following vasectomy. This is generally believed to be caused if the epididymis becomes congested with dead sperm and fluid. It usually disappears within six months.
Congestion - a common name for chronic orchalgia.
Back to top
Ejaculation - the discharge of seminal fluid at the moment of male sexual climax.
Ejaculation, retrograde - seminal discharge into the bladder rather than out the tip of the penis through the urethra.
Epididymis - tightly coiled, very small tubes covering the back and sides of the testis, where sperm are stored and mature after leaving the testis. From the epididymis, sperm migrate to the vas deferens.
Epididymitis - pain and/or swelling of the epididymis. The application of heat, the use of a scrotal supporter, and the use of anti-inflammatory medication and sometimes antibiotics usually clear this uncommon condition within a week.
Erectile Dysfunction - the inability for a sexually active male to obtain and sustain an erection for sexual purposes. Also called impotence.
Erection - state of male arousal in which the penis fills with blood, becomes turgid and hard.
Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH) - a pituitary (gland within the brain) hormone that stimulates the testes to make sperm.
Hematoma - bleeding inside the scrotum that may cause painful swelling shortly following a vasectomy. While seldom serious, it should be reported to a physician.
Hematospermia - the presence of blood in a mans ejaculation. Usually it is a benign condition due to a small ruptured blood vessel, and is usually of no consequences. Occasionally it may be related to an infection and can be treated with antibiotics.
Hydrocele - a collection of fluid around the testicle that causes a painless swelling, and is common to men in middle age.
Back to top
Immune Reactions - following vasectomy, the immune system may recognize the absorbed sperm cells as foreign proteins and produce antibodies in response.
Impotence - also called erectile dysfunction; a condition of being unable to maintain an erection to ejaculate.
Infection - if blood collects under the skin following vasectomy, it can become infected, resulting in painful inflammation. Infection of the incision site, or deeper tissue, occurs in less than 5 percent of all cases. Such infections respond favorably to antibiotic treatment, antimicrobial creams and hot baths, usually within a week.
Infertility - partial or complete inability to cause or achieve pregnancy. The male factors are poor or no sperm count, poor sperm motility (movement) often seen with a varicocoele, and infection or obstruction of the vas deferens tube.
Inguinal Area - the abdominal region, common to hernia. Inadvertent blockage of the vas deferens may be the result of prior inguinal hernia surgery.
Insemination- semen successfully placed within the uterus, cervix or vagina.
Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI)- an in vitro fertilization procedure that requires the direct injection of a single sperm into an ovum to conceive.
In Vitro Fertilization (IVF)- a treatment for infertility in which a womans egg and a suspension of sperm are incubated together in a culture dish (like a test tube), wherein fertilization occurs outside the female body. Once embryos are formed, they are placed back into the womans uterus.
Libido - sexual desire.
Long-term Testicular Pain- postoperative testicular pain lasting longer than three months. Persistent testicular discomfort is rare. This uncommon complication may be the result of pinched nerves.
Back to top
MESA - a general term usually referring to Microsurgical Epididymal Sperm Aspiration; see Sperm Aspiration.
Microsurgery - surgery using optical magnification provided by an operating microscope.
Microsurgical Fertilization- a procedure used to facilitate sperm penetration into the oocyte (the female egg); fertilization takes place under the microscope - also known as Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (see above).
Motility - movement of the sperm. Less motility means less chance of fertility.
Multiple Semen Analysis - the collection of at least two semen examples on separate days to examine consistency or discrepancies in the semen parameters of sperm count, sperm motility, sperm morphology (shape), semen volume, etc. A single semen analysis is not always representative of the "typical" semen from an individual male, as the semen parameters can fluctuate from specimen to specimen, from day to day, from season to season, and perhaps most importantly from lab to lab.
No-Scalpel Vasectomy (NSV) - a procedure which utilizes special instruments to puncture the scrotal skin and draw the vas out to allow it to be cut and tied. There is very little bleeding in this less invasive method of vasectomy, and in many cases, no stitches are necessary. Less pain and fewer complications are associated with No-Scalpel Vasectomy.
Oligospermia - abnormally low numbers of sperm in the semen.
Orchiectomy - surgical removal of one or both of the testicles.
Orchitis - painful inflammation or swelling of the testicle sometimes due to an infection.
Back to top
Postoperative Pain - some degree of scrotal pain or ache is normal following a vasectomy. Painful discomfort normally disappears within a day or two, while a slight ache may remain slightly longer.
Premature Ejaculation (PE) - The inability to refrain from ejaculation prior to insertion of the penis into the vagina, or within only a few minutes of penetration such that the sexual encounter is unsatisfactory for the couple, and or deposition of sperm within the vagina in not able to be achieved reliably.
Priapism - persistent erection of the penis, usually accompanied by tenderness and pain.
Prostatalgia - pain in the prostate gland.
Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) - an antigen made by the prostate gland and found in the blood; an abnormal level may indicate cancer in the prostate gland.
Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) Blood Test - a blood test used to help detect prostate cancer by measuring a substance called prostate-specific antigen produced by the prostate. PSA is frequently elevated in prostate cancer and can be the first sign of this illness.
Prostate Gland - located below the bladder, the gland that contributes to seminal secretions and where the ejaculatory ducts, the vas deferens and the urethra join. Urine released from the bladder flows through this channel running through the center of this gland to enter the urethra of the penis.
Prostatitis - inflammation of the prostate gland, sometimes caused by infection.
Prostate and Testicular Cancer - there is no known increased risk of testicular cancer following vasectomy. However, artificially increased levels of testosterone over the long term are associated with an increased risk of prostate cancer. While there were earlier studies that suggested a possible relationship between vasectomy and prostate cancer, more recent studies do not support any causative relationship. Nevertheless, physicians agree that all men over the age of 50 should have regular prostate examinations and PSA blood testing.
Recanalization - spontaneous rejoining of the severed vas connection through the scar tissue. This can be detected by semen testing at regular intervals.
Back to top
Scrotal Support - ("jock strap") a device, such as an athletic supporter, worn after vasectomy and reversal to decrease swelling and pain.
Scrotum - the sac that contains the testicles, epididymis and vas deferens.
Semen - the combination of sperm and glandular fluid released out of the urethra when a man ejaculates; normally a mixture of less than 1 percent sperm and 99 percent seminal fluid.
Seminal Vesicle - a gland that produces a component of seminal secretions, the fluid that is ejaculated by a man at sexual climax. The fluid transports and nourishes the sperm.
Sexually Transmitted Disease (STD) - infection that is most commonly spread through sexual intercourse and other intimate sexual and genital contact.
Sperm Aspiration - a general term usually referring to Microsurgical Epididymal Sperm Aspiration (MESA), a surgical procedure whereby live sperm are attempted to be extracted from the epididymis and preserved for in-vitro fertilization (IVF). MESA may be considered for men when the reproductive tract is blocked. Done under a microscope, the surgery is relatively safe,. Surgically retrieved sperm cannot be used for artificial insemination (intrauterine insemination), but must be used with ICSI (intra-cytoplasmic sperm injection) and IVF (in vitro fertility). Only ejaculated sperm will work with artificial insemination-either fresh or frozen/thawed.
Sperm Banking - the process of collecting (via ejaculation, electroejaculion, or surgically) and preserving sperm for possible future use. Typically, sperm samples are frozen in liquid nitrogen and can be stored for extended periods before thawing and used in assisted reproduction techniques such as artificial insemination or in vitro fertilization. Normally, there is a continuing cost for the storage service.
Sperm Disorders - problems with the production and maturation of sperm; a cause of male infertility. Sperm may be immature, abnormally shaped or unable to move properly.
Sperm Granulomas - a small and usually painless lump at the site of a vasctomy and caused by sperm leakage from the cut end of the vas. This does not pose a danger and usually resolves over time. Rarely, the immune system responds to sperm leakage with an inflammatory reaction. This reaction frequently resolves with the use of anti-inflammatory medication. The presence of a sperm granuloma can be a predictor of success for a vasectomy reversal.
Sterility - the physical inability to reproduce due to infertility.
Suture - the material (thread) used during vasectomy and vasectomy reversal surgery.
Back to top
Testes - ( testicles) located in the scrotum, the male reproductive glands that produce sperm and testosterone.
Testicles - see testes. Testicular Cancer - cancer that develops in a testicle.
Testosterone - the sex hormone produced by the male sex glands, which stimulates and controls the development of the reproductive organs, as well as male characteristics, including body and facial hair, low voice and muscle growth. Testosterone is very important for sperm production within the testicles.
Tubal Ligation - female sterilization surgery where the uterine tubes are cut and closed by ligation or various mechanical devices. A more extensive surgery than male sterilization (vasectomy) and done under general anesthetic.
Urethra - the passageway running from the bladder to the penis, which carries urine and semen outside the body.
Urology - a medical specialty for the diagnosis, treatment and surgical care of problems of the male and female urinary tract and the male reproductive system. Urology covers diagnosis and treatment for both adults and children. A urologist is a medical doctor with specialized surgical training in these areas.
Back to top
Varicocoele - a dilation of the veins draining blood from the testicle back to the body. This increases blood and heat around the testicle, causing injury to the sperm. A varicocoele can be treated with surgery or interventional radiology (see Varicocele Embolization).
Varicocele Emboliza ion - nonsurgical, outpatient interventional radiology procedure in which the varicocele is occluded or "closed off" with a balloon catheter or vessel-hardening (sclerosing) solution.
Varicocelectomy - surgical correction of a varicocele.
Vas Deferens - the two muscular tubes that carry sperm from the testicle and epididymis to the urethra of the prostate. Each tube is referred to as a Vas. Together, they are called Vasa.
Vas Remnant - the length of the vas deferens from the epididymis to the site of the vasectomy.
Vasectomy - a surgical procedure that produces infertility by blocking the transport of sperm through the vas deferens.
Vasoepididymostomy - a surgical procedure that reverses a vasectomy in the case where there is a second blockage due to scar tissue in the epiddymis, in addition to the scar tissue from the vasectomy procedure. In this procedure the vas deferens is reconnected to the epididymis so as to bypass both scars.
Vasovasostomy - conventional vasectomy reversal. A surgical procedure to restore fertility by reconnecting the ends of vas deferens that were severed when vasectomy was performed.
Back to top